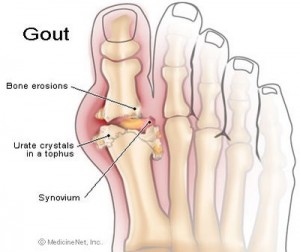
Gout is a disease that results from an overload of uric acid in the body. This overload of uric acid leads to the formation of tiny crystals of urate that deposit in tissues of the body, especially the joints. When crystals form in the joints, it causes recurring attacks of joint inflammation (arthritis). Gout is considered a chronic and progressive disease. Chronic gout can also lead to deposits of hard lumps of uric acid in the tissues, particularly in and around the joints and may cause joint destruction, decreased kidney function, and kidney stones(nephrolithiasis)
The treatment of an acute attack of gouty arthritis involves measures and medications that reduce inflammation. Preventing future acute gout attacks is equally as important as treating the acute arthritis. Prevention of acute gout involves maintaining adequate fluid intake, weight reduction, dietary changes, reduction in alcohol consumption, and medications to lower the uric acid level in the blood.
Maintaining adequate fluid intake helps prevent acute gout attacks. Adequate fluid intake also decreases the risk of kidney stone formation in patients with gout. Alcohol is known to have diuretic effects that can contribute to dehydration and precipitate acute gout attacks. Alcohol can also affect uric acid metabolism to cause hyperuricemia. Therefore, alcohol has two major effects that worsen gout by slowing down the excretion of uric acid from the kidneys as well as by causing dehydration, both of which contribute to the precipitation of uric acid crystals in the joints.
© 2021 Singapore Orthopaedic Centre for Spine & Sports Medicine. All Rights Reserved.
Designed By ArsEmporium.com
Connect with Us




